Introduction
In today’s rapidly changing world, education must keep pace with technological progress. Arduino, an open-source electronics platform, offers a powerful and accessible way for students to explore programming, engineering, and creative problem-solving. By combining coding with hands-on experimentation, Arduino helps learners develop not only technical knowledge but also essential skills for the future, such as collaboration, creativity, and critical thinking.
1. The Cognitive and Creative Benefits of Arduino
- Problem-Solving and Analytical Thinking: Programming Arduino devices requires students to identify errors, design logical solutions, and test their ideas in real time. This process strengthens their systematic thinking abilities.
- Creativity and Innovation: With Arduino boards and sensors, learners can design unique projects, from automated plant watering systems to interactive art. This stimulates imagination and encourages innovative approaches.
- Interest in STEM Subjects: Since Arduino involves concepts from physics, mathematics, and computing, it naturally increases students’ curiosity about science and technology.
2. Collaboration and Social Skills
Most Arduino projects are carried out in teams. This fosters:
- Communication and teamwork.
- Sharing responsibilities and working toward common goals.
- Peer learning, where students help each other to debug code or design circuits.
These skills are transferable beyond the classroom, preparing students for future academic and professional challenges.
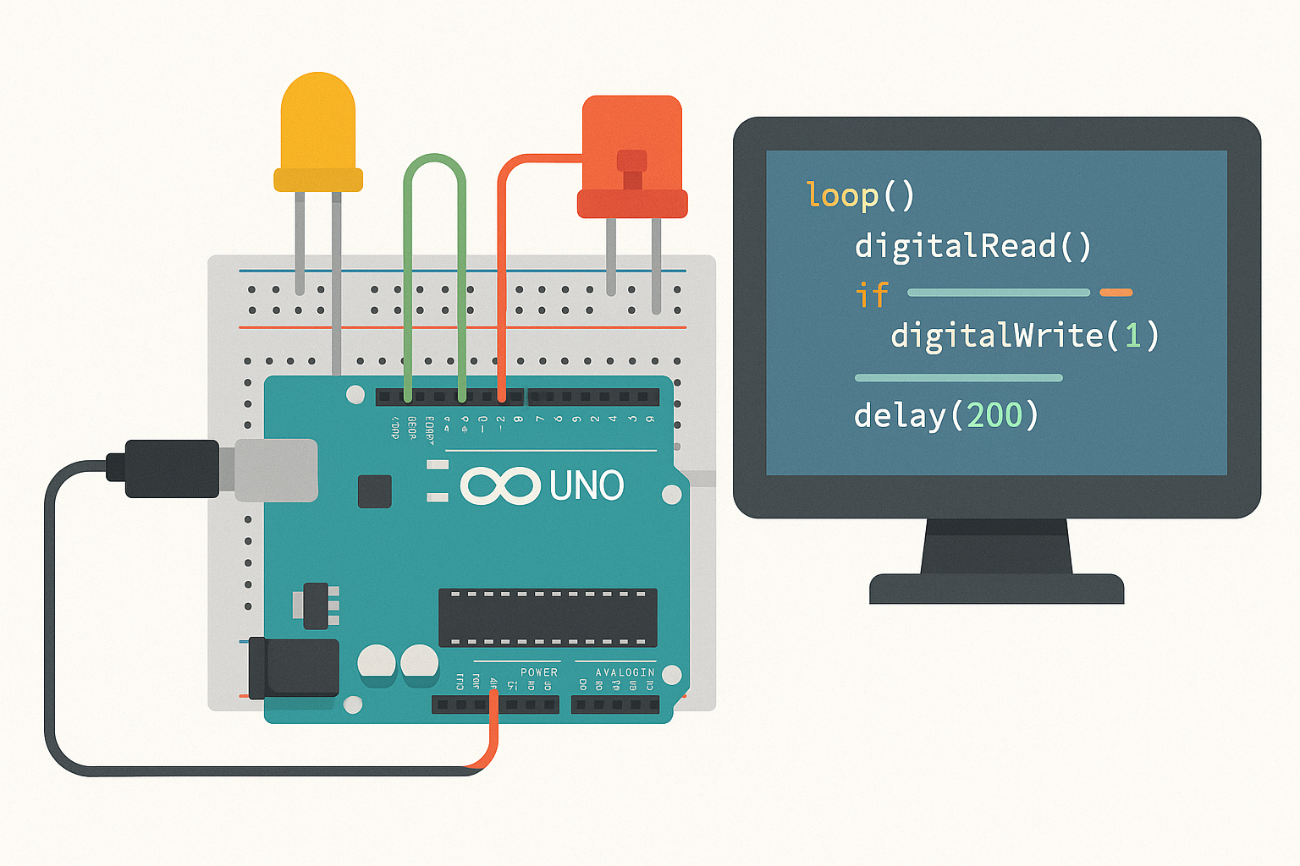
3. Preparing Students for the Future
Arduino education plays a key role in equipping young people for tomorrow’s world:
- Digital Literacy: Students become familiar with hardware and software integration.
- STEM Competences: Building with Arduino connects science, technology, engineering, and mathematics in a multidisciplinary way.
- Entrepreneurship and Innovation: Project-based learning and competitions encourage students to transform ideas into practical solutions, sparking an entrepreneurial mindset.
4. From Classroom Projects to Real-World Impact
Arduino can be used to build smart devices, explore the Internet of Things (IoT), and even integrate artificial intelligence. For example, learners can create systems that respond intelligently to their environment, such as temperature-controlled fans or automated lights.
These experiences show students that what they learn in school can have real applications in society.
Conclusion
Arduino is more than a tool for learning how to code; it is a bridge to creativity, problem-solving, and future employability. By integrating Arduino into education, schools can cultivate a generation of innovators capable of shaping the technological world of tomorrow.

